Do youKnow AboutHuntite???

LetsKnow itTogether!!!
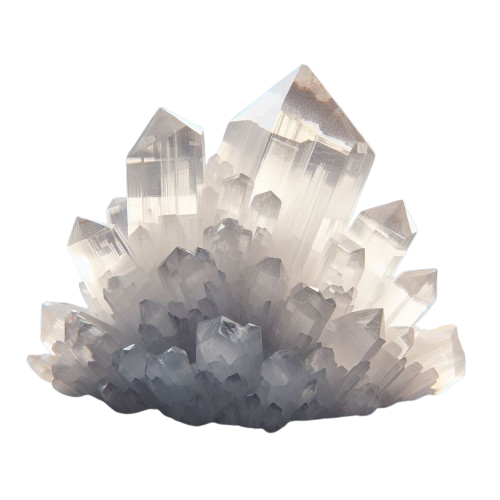
What is Huntite ?
Huntite is a naturally occurring mineral composed of hydromagnesite and calcite. It is typically found in sedimentary environments and often occurs alongside other minerals such as dolomite and magnesite. With its characteristic white, gray, or colorless appearance, huntite exhibits a unique blend of elegance and utility.


Uses of Huntite
Huntite finds application in various industries due to its unique properties. From ceramics to plastics, it serves as a versatile filler material, enhancing the performance and durability of products. Additionally, its presence in soil stabilization and environmental remediation projects underscores its importance beyond the industrial realm.
why choose huntite
Chemical Composition
Huntite is a carbonate mineral with the chemical formula CaMg_3(CO_3)_4. It is a member of the calcite group of minerals and belongs to the trigonal crystal system
Historical Use
Initially used as a white pigment , Decorative Arts, Ceramics and Pottery, Scientific Research , Soil Stabilization , Environmental Remediation , Cultural and Ritual Practices

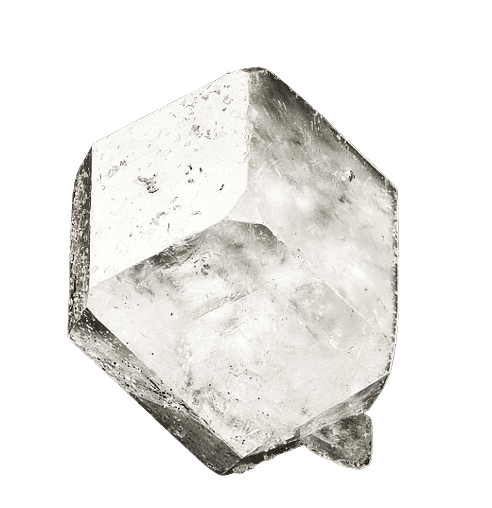
Crystal Structure
Huntite crystallizes in the trigonal crystal system, typically forming rhombohedral or scalenohedral crystals. However, it can also occur in massive, granular, or fibrous forms
Physical Properties
Huntite typically appears as white, gray, or colorless crystals with a vitreous to pearly luster. It has a Mohs hardness of around 3 to 4 and exhibits perfect rhombohedral cleavage
extra information
- Discovered in 1953 by George Faust.
- Named after Professor Walter Frederick Hunt.
- Occurs alongside other Mg/Ca carbonates.
- Found in various environments globally.
- Fire Retardant: Releases water and CO2 when heated, helping to suppress flames in plastics and coatings.
- Ceramics: Enhances strength and durability in ceramic products.
- Pigment: Historically used to provide bright white color and opacity in paints and coatings.
- Plastic Filler: Improves material properties and reduces production costs in plastic manufacturing.
- Carbon Sequestration: Captures and stores CO2, helping mitigate climate change effects.
- Decorative Stone: Used in mosaics and ornamental stonework for its attractive appearance.
- Educational Tool: Serves as a practical example in teaching mineralogy and geology.
- Discovery: Huntite specimens are often found in sedimentary environments.
- Identification: Recognize huntite by its white to gray color and trigonal crystal structure.
- Locations: Look for huntite in areas with magnesium-rich rocks and carbonate deposits.
- Tools: Bring basic tools like a rock hammer, chisel, and safety gear for collecting.
- Safety: Exercise caution when collecting huntite in remote or rugged terrain.
- Ethics: Follow local regulations and respect private property when collecting specimens.
- Preservation: Handle huntite specimens carefully to preserve their natural beauty and integrity.
- Documentation: Keep records of where and when specimens were collected for future reference.
- Global Supply: Major suppliers of huntite include countries with significant mineral deposits, such as Turkey, the USA, and China.
- Industrial Demand: The demand for huntite is driven by its use in fire retardants, ceramics, and as a filler in plastics.
- Market Value: The value of huntite varies based on its purity, crystal size, and specific industrial application.
- Trade Dynamics: Huntite is traded globally, with fluctuations in price influenced by mining output and industrial needs.
- Economic Importance: Huntite contributes to the economy through its role in manufacturing and environmental applications.
- Regulatory Factors: Trade and mining of huntite are subject to environmental and safety regulations in different countries.
some reviews



Whether you're a collector, artisan, or industry professional, there's something for everyone in the world of huntite. Start exploring and unlock the possibilities today!
Dive into the fascinating world of huntite and discover its beauty, versatility, and practical applications. Start exploring now!
Explore now !